Understanding the Latest Updates on Staffing Requirements in Long-Term Care Facilities
See My Story
Through professional keynote speaking and the KrisBHarmony Series, Kris is able to reach millions of viewers engaging in powerful conversations about ensuring systematically marginalized persons have a voice at the table.
Kris is a nationally recognized keynote speaker with more than 32 years of experience in the healthcare industry, with a specialty in the Post-Acute Care Arena. She has an Occupational Therapist degree from Tufts...
Read More →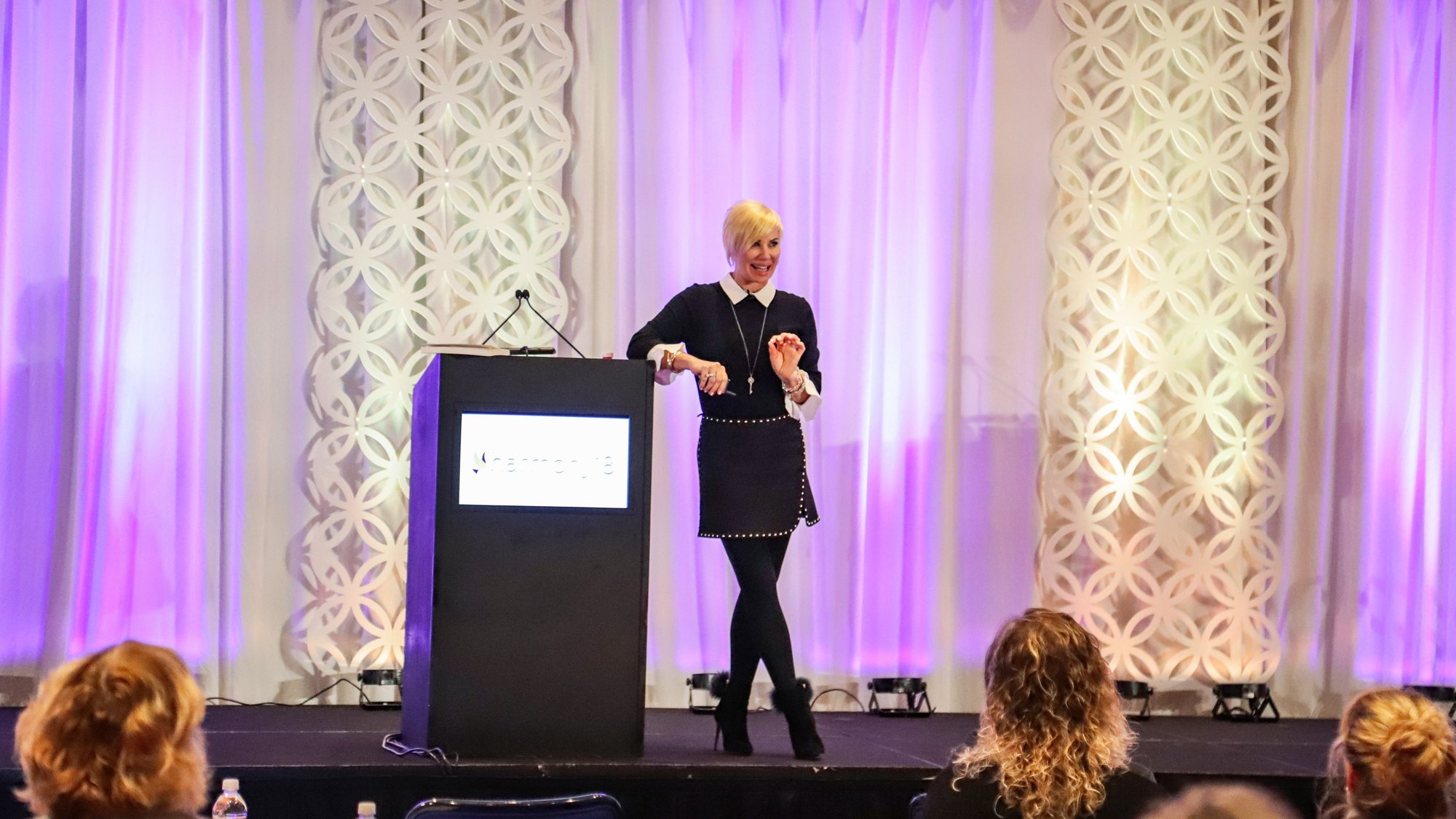
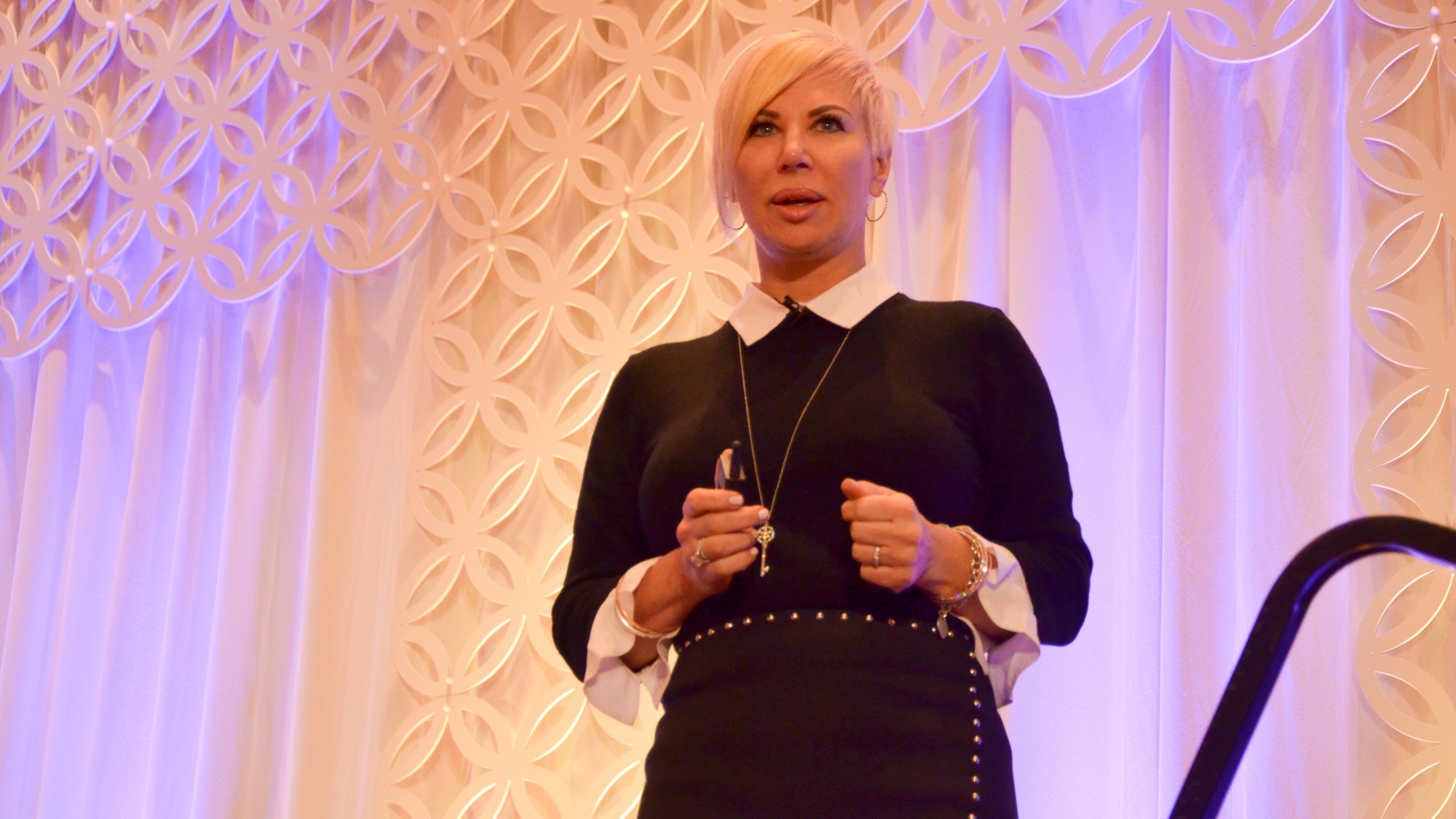

On Tuesday, September 12,2023 hundreds of individuals gathered in perron and via zoom at the Massachusetts State House to attend and testify on multiple bills. The hearing lasted approximately 7 hours. I attended the entire session and would like to share highlights that I feel will help many individuals gain a better understanding of the ongoing issues within the legal system...
Read More →
.png?width=208&name=Logo-KrisB%20(1).png)
Empowering People who are systematically marginalized and impacting changes in our laws, our culture, and society.
KrisBHarmony, LLC
Summerlin, Nevada
(617) 595-6032
kris@krisbharmony.com
© 2024 KrisBHarmony, LLC. All Rights Reserved.